What is a Campaign? Definition & Examples
In today’s fast-paced marketing landscape, understanding campaigns isn’t just helpful—it’s essential for business success. Whether you’re launching a new product, building brand awareness, or driving conversions, campaigns serve as the strategic backbone of modern marketing efforts. This comprehensive guide explores what campaigns are, how they work, and how you can leverage them effectively.
What is a Campaign?
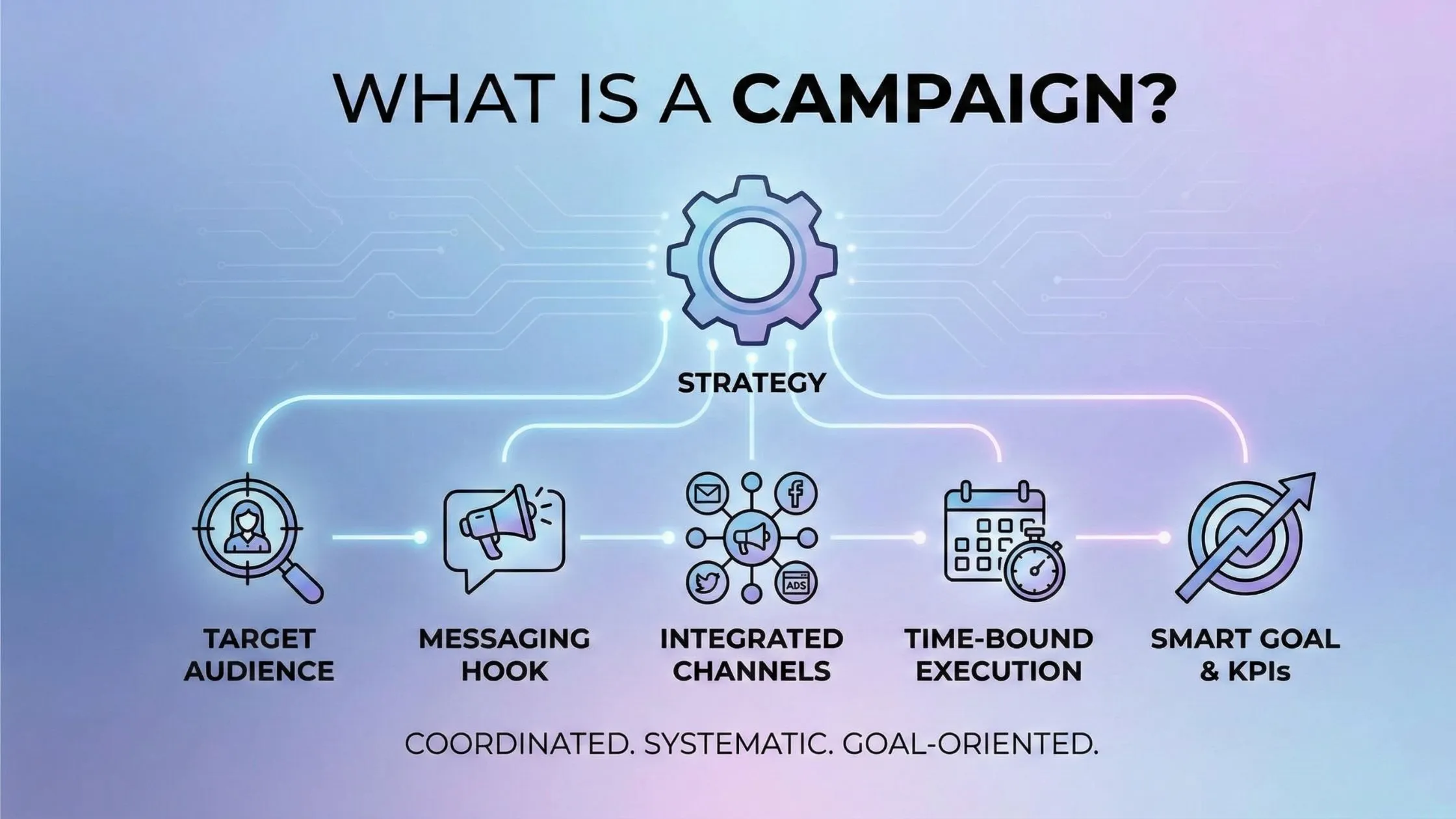
A campaign is a coordinated series of strategic activities designed to achieve specific business objectives within a defined timeframe. Unlike isolated marketing activities, campaigns unite multiple touchpoints, messages, and channels into a cohesive effort that drives measurable results.
Think of a campaign as a story told across different chapters. Each chapter—whether it’s a social media post, email blast, or billboard—contributes to the larger narrative while maintaining consistency in messaging and purpose.
Key Characteristics of Campaigns
- Strategic Planning: Every successful campaign begins with clear objectives, target audience identification, and resource allocation.
- Multi-Channel Approach: Modern campaigns leverage various platforms—from digital channels like social media and email to traditional mediums like print and television.
- Time-Bound Execution: Campaigns run for specific durations, creating urgency and allowing for performance measurement.
- Measurable Outcomes: Success is tracked through key performance indicators (KPIs) that align with campaign objectives.
- Unified Messaging: All campaign elements communicate a consistent message that reinforces the core value proposition.
Types of Marketing Campaigns
Understanding different campaign types helps you choose the right approach for your objectives:
1. Brand Awareness Campaigns
These campaigns focus on introducing your brand to new audiences and increasing visibility. They emphasize emotional connection and brand recognition rather than immediate conversions.
When to use: Launching a new brand, entering new markets, or repositioning an existing brand.
2. Product Launch Campaigns
Designed to introduce new products or services to the market, these campaigns generate excitement and drive initial adoption.
When to use: Releasing new offerings, unveiling product updates, or expanding product lines.
3. Lead Generation Campaigns
These campaigns capture potential customer information through gated content, webinars, free trials, or consultations.
When to use: Building sales pipelines, expanding customer databases, or nurturing prospects.
4. Conversion Campaigns
Focused on turning prospects into paying customers, these campaigns emphasize clear calls-to-action and value propositions.
When to use: Driving immediate sales, promoting limited-time offers, or boosting revenue.
5. Customer Retention Campaigns
These efforts keep existing customers engaged, encourage repeat purchases, and build long-term loyalty.
When to use: Reducing churn, increasing lifetime value, or strengthening customer relationships.
6. Rebranding Campaigns
When businesses evolve, rebranding campaigns communicate changes in positioning, values, or visual identity.
When to use: Mergers and acquisitions, market pivots, or modernizing outdated brand images.
7. Seasonal Campaigns
Timed around holidays, events, or specific seasons, these campaigns capitalize on predictable consumer behavior patterns.
When to use: Holiday shopping seasons, back-to-school periods, or industry-specific events.
How to Create an Effective Campaign
Creating campaigns that deliver results requires methodical planning and execution. Follow this comprehensive framework:
1. Define Clear Objectives
Start with SMART goals (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound). Instead of vague aims like “increase visibility,” set precise targets such as “increase website traffic by 35% within three months.”
Common campaign objectives include:
- Generating a specific number of qualified leads
- Achieving target revenue figures
- Reaching defined audience segments
- Improving brand sentiment scores
- Increasing customer acquisition or retention rates
2. Understand Your Target Audience
Deep audience understanding separates successful campaigns from ineffective ones. Develop detailed buyer personas that include:
- Demographics: Age, gender, location, income level, education, occupation
- Psychographics: Values, interests, lifestyle choices, pain points, aspirations
- Behavioral Patterns: Purchase behaviors, content consumption habits, preferred communication channels
- Customer Journey Stage: Awareness, consideration, decision, retention
Use market research, customer surveys, social listening, and analytics data to build accurate audience profiles.
3. Craft Compelling Messages
Your campaign message should resonate emotionally while clearly communicating value. Effective messages:
- Address specific audience pain points
- Highlight unique benefits and differentiation
- Use language that speaks directly to your audience
- Create emotional connections that drive action
- Include clear, persuasive calls-to-action
4. Select the Right Channels
Channel selection determines campaign reach and effectiveness. Consider where your audience spends time and how they prefer to receive information:
Digital Channels:
- Social media platforms (Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, TikTok, X)
- Email marketing and automation
- Search engine marketing (SEO and PPC)
- Display advertising and retargeting
- Content marketing and blogs
- Video platforms (YouTube, streaming services)
Traditional Channels:
- Television and radio advertising
- Print media (newspapers, magazines)
- Direct mail campaigns
- Outdoor advertising (billboards, transit ads)
- Event sponsorships and activations
Emerging Channels:
- Influencer partnerships
- Podcast advertising
- Connected TV and streaming ads
- Virtual and augmented reality experiences
5. Develop a Content Strategy
Content fuels campaign execution. Create a content calendar that maps specific assets to campaign phases:
- Pre-Launch Phase: Teaser content, behind-the-scenes glimpses, anticipation-building posts
- Launch Phase: Announcement content, hero assets, high-impact creative
- Mid-Campaign: Supporting content, user-generated content, testimonials, educational materials
- Post-Campaign: Results sharing, thank-you messages, continued engagement content
6. Set a Realistic Budget
Allocate resources across campaign elements:
- Creative development and production
- Media buying and advertising spend
- Technology and tools
- Personnel and agency costs
- Contingency funds for optimization
Balance paid, owned, and earned media to maximize ROI while staying within budget constraints.
7. Establish Measurement Framework
Before launching, determine how success will be measured. Define primary and secondary KPIs:
- Awareness Metrics: Impressions, reach, brand lift, social media mentions
- Engagement Metrics: Click-through rates, time on site, social engagement, content downloads
- Conversion Metrics: Lead generation, sales, sign-ups, purchases
- Retention Metrics: Customer lifetime value, repeat purchase rate, churn rate
8. Execute with Precision
Launch your campaign according to plan while maintaining flexibility for real-time adjustments. Monitor performance continuously and optimize underperforming elements.
9. Analyze and Learn
Post-campaign analysis provides crucial insights for future efforts:
- Compare results against objectives
- Identify top-performing channels and creative
- Understand what resonated with audiences
- Document lessons learned
- Calculate return on investment
- Gather customer feedback
Common Campaign Mistakes to Avoid
Even experienced marketers make these critical errors:
1. Skipping Audience Research
Assuming you know your audience without data validation leads to misaligned messaging and wasted resources. Always validate assumptions through research.
2. One-Size-Fits-All Approach
Repurposing the same campaign without adaptation ignores evolving audience needs, market dynamics, and seasonal trends. Customize campaigns based on current data and feedback.
3. Neglecting A/B Testing
Launching full-scale campaigns without testing variations in messaging, design, or channels is like serving food without tasting it first. Test with audience segments before going all-in.
4. Dropping Post-Campaign Communication
Ending engagement when campaigns conclude wastes momentum. Continue conversations through follow-ups, surveys, thank-you messages, or exclusive offers.
5. Overcomplicating Messages
Complex, convoluted messaging loses audience attention. Keep communications clear, concise, and compelling. Simple messages often deliver stronger impact.
6. Ignoring Mobile Optimization
With mobile devices accounting for majority of digital consumption, failing to optimize for mobile experiences is a critical oversight that reduces effectiveness.
7. Setting Unrealistic Expectations
Overpromising results or setting unattainable goals sets campaigns up for failure. Base expectations on historical data, industry benchmarks, and realistic resource allocation.
The Role of Technology in Modern Campaigns
Campaign success increasingly depends on strategic technology use:
1. Marketing Automation Platforms
Automation tools streamline repetitive tasks, enabling personalized communication at scale while freeing teams for strategic work.
2. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems
CRMs centralize customer data, enabling better segmentation, personalized outreach, and comprehensive customer journey tracking.
3. Analytics and Attribution Tools
Advanced analytics platforms provide real-time performance insights, helping marketers understand which touchpoints drive conversions and optimize accordingly.
4. Content Management Systems
CMS platforms enable efficient content creation, distribution, and optimization across multiple channels while maintaining brand consistency.
5. Social Media Management Tools
These platforms consolidate social posting, monitoring, and engagement across multiple networks, improving efficiency and response times.
6. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI powers predictive analytics, content personalization, chatbots, and automated optimization that enhance campaign performance.
Campaign Planning Timeline
Successful campaigns require adequate planning time:
3-6 Months Before Launch:
- Define objectives and strategy
- Conduct audience research
- Develop creative concepts
- Secure budget approval
- Build campaign infrastructure
2-3 Months Before Launch:
- Create campaign assets
- Develop content calendar
- Set up tracking and analytics
- Conduct internal reviews
- Brief all stakeholders
1 Month Before Launch:
- Finalize all creative assets
- Test technical implementations
- Train relevant teams
- Begin teaser content
- Prepare launch materials
Launch Week:
- Execute coordinated launch
- Monitor performance closely
- Address any technical issues
- Engage with audience responses
Post-Launch:
- Optimize based on performance data
- Adjust budget allocation
- Create responsive content
- Maintain momentum
Campaign Conclusion:
- Compile final reports
- Analyze results thoroughly
- Document lessons learned
- Thank participants and contributors
- Plan follow-up activities
Measuring Campaign Success
Comprehensive measurement requires tracking multiple metric categories:
Quantitative Metrics
Reach and Awareness:
- Total impressions delivered
- Unique users reached
- Share of voice in category
- Brand recall and recognition
Engagement:
- Click-through rates
- Social media interactions
- Video completion rates
- Content downloads
Conversions:
- Lead generation volume
- Sales revenue attributed
- Cost per acquisition
- Conversion rate by channel
Return on Investment:
- Total revenue generated
- Customer lifetime value
- Return on ad spend
- Marketing efficiency ratio
Qualitative Metrics
- Brand Sentiment: Monitor social listening, review analysis, and survey feedback to understand how campaigns affect brand perception.
- Customer Feedback: Direct customer input through surveys, focus groups, and interviews provides insights beyond numerical data.
- Competitive Positioning: Assess how campaigns affect market position relative to competitors.
- Media Coverage: Earned media value and quality of coverage indicate campaign cultural impact.
The Future of Campaign Marketing
Campaign strategies continue evolving with technological advancement and changing consumer behaviors:
1. Increased Personalization
Advanced data analytics and AI enable hyper-personalized campaigns that speak to individual preferences and behaviors at scale.
2. Privacy-First Approaches
With increasing privacy regulations and third-party cookie deprecation, campaigns must rely more on first-party data and contextual targeting.
3. Immersive Experiences
Virtual reality, augmented reality, and interactive content create engaging experiences that traditional campaigns cannot match.
4. Sustainability Focus
Consumers increasingly prefer brands demonstrating environmental and social responsibility. Purpose-driven campaigns resonate more strongly.
5. Short-Form Video Dominance
Platforms like TikTok and Instagram Reels continue prioritizing short-form video content, requiring campaigns to adapt to these formats.
6. Influencer Integration
Authentic influencer partnerships replace traditional celebrity endorsements, providing credibility and access to engaged communities.
7. Real-Time Marketing
Brands increasingly respond to cultural moments and trending topics in real-time, requiring agile campaign capabilities.
Key Takeaways
Campaigns represent coordinated strategic efforts that drive specific business outcomes through integrated multi-channel approaches. Success requires:
- Clear, measurable objectives aligned with business goals
- Deep understanding of target audiences and their preferences
- Compelling messages that resonate emotionally while communicating value
- Strategic channel selection based on audience behaviors
- Continuous performance monitoring and optimization
- Comprehensive post-campaign analysis for ongoing improvement
Whether you’re a small business owner launching your first campaign or a marketing professional refining advanced strategies, understanding campaign fundamentals empowers you to create initiatives that capture attention, drive engagement, and deliver measurable business results.
The most effective campaigns balance creativity with strategy, intuition with data, and consistency with adaptability. By following the frameworks outlined in this guide while remaining flexible enough to respond to real-time feedback, you can create campaigns that not only achieve immediate objectives but also build lasting brand equity and customer relationships.
Remember: every great campaign starts with thorough planning, executes with precision, and concludes with careful analysis that informs future success. The campaign you’re planning today could become tomorrow’s case study in marketing excellence.

With 5+ years of SEO experience, I’m passionate about helping others boost their online presence. I share actionable SEO tips for everyone—from beginners to experts.


